Security
QuickStart Module
This quickstart module shows you how to perform authentication and use security tokens
Authentication
In order to use the API in any programming language, you need to be able to generate an ID Token to identify yourself to the services. This token is issued by Microsoft using your Azure Active Directory and is scoped to the OpenDataDSL API:
scope=api://opendatadsl/.default
The method you use to generate the token is determined by how the application or script will be run.
| Application Type | Generation Method |
|---|---|
| User application, attended login | User log in via Web Browser |
| System application, unattended login | Use secret key specific for the application |
Unattended Login
For an unattended login, you will need to create an application in Azure AD and generate a secret. The 3 pieces of information required are:
- You company tenant id - tid
- The id of the application in Azure AD - aid
- The generated secret - sid
Getting the necessary id's and secret
The 3 items above can be retrieved/generated in Azure Active Directory as follows:
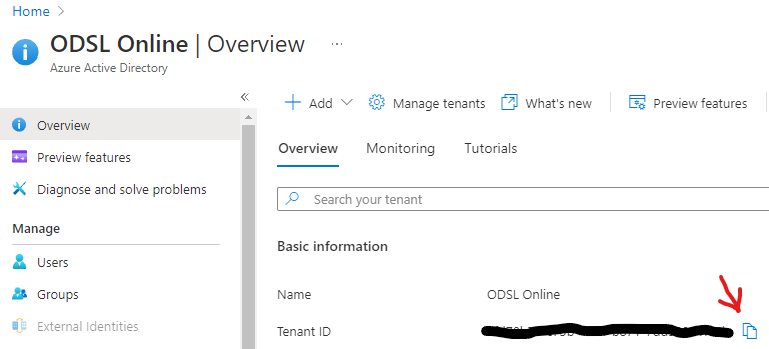
Tenant ID
Log into Azure Active Directory, with your tenant selected in Overiew, you should see your tenant id on the main page.
Click the copy icon next to the Tenant ID and paste it somewhere safe for later as tid.
Client ID
If you haven't created a new App Registration in Azure Active Directory, you will need to do that now in order to get the application id and generate a secret.
Once you have created your App Registration, click on it so that you are in the Overview screen and copy the Application (client) ID and paste it somewhere safe for later as aid.
Secret
To generate a secret, whilst in the App Registration, click on the Certificates and Secrets menu item.
Create a new client secret, then immediately copy the secret and paste it somewhere safe for later as sid.
Example of getting an Access Token
- REST
- Python
- Java
GET /{{tid}}/oauth2/v2.0/token
Host: login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=client_credentials&
client_id={{aid}}&
client_secret={{sid}}&
scope=api://opendatadsl/.default
import requests
tid = "enter your tenant id"
aid = "enter your app id"
sid = "enter your secret"
url = "https://login.microsoftonline.com/{}/oauth2/v2.0/token".format(tid)
payload = {
'grant_type':'client_credentials',
'client_id':'{}'.format(aid),
'client_secret':'{}'.format(sid),
'scope':'api://opendatadsl/.default'
}
headers = {'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
response = requests.get(url, data=payload, headers=headers)
token = response.json()['access_token']
An example class to retrieve an Access Token - replace {{tid}}, {{aid}} and {{sid}} with the tokens you saved above.
package com.opendatadsl.security;
import com.microsoft.aad.msal4j.ClientCredentialFactory;
import com.microsoft.aad.msal4j.ClientCredentialParameters;
import com.microsoft.aad.msal4j.ConfidentialClientApplication;
import com.microsoft.aad.msal4j.IAuthenticationResult;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class UnattendedClient {
private final static String APP_ID = "{{aid}}";
private final static String SECRET = "{{sid}}";
private final static String TID = "{{tid}}";
private final static String AUTHORITY = "https://login.microsoft.com/" + TID;
private final static Set<String> SCOPE = Collections.singleton("api://opendatadsl/.default");
private static IAuthenticationResult result = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String token = new UnattendedClient().getToken();
System.out.println("Access token: " + token);
}
public String getToken() throws Exception {
if (result == null || hasExpired()) {
result = getAccessTokenByClientCredentialGrant();
}
return result.accessToken();
}
private boolean hasExpired() {
if (result != null) {
if (result.expiresOnDate().getTime() < System.currentTimeMillis())
return true;
return false;
}
return true;
}
private IAuthenticationResult getAccessTokenByClientCredentialGrant() throws Exception {
ConfidentialClientApplication app = ConfidentialClientApplication.builder(
APP_ID,
ClientCredentialFactory.createFromSecret(SECRET))
.authority(AUTHORITY)
.build();
ClientCredentialParameters clientCredentialParam = ClientCredentialParameters.builder(SCOPE)
.build();
CompletableFuture<IAuthenticationResult> future = app.acquireToken(clientCredentialParam);
IAuthenticationResult r = future.get();
return r;
}
}
Using the token
Once you have the token, you need to add it into an Authorization header with the prefix Bearer:
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
Example request using the token
This example request gets information about the Object service.
- REST
- Python
- Java
GET https://api.opendatadsl.com/api/object
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
headers = {'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token)}
response = requests.get('https://api.opendatadsl.com/api/object', headers=headers)
print(response.json())
URL u = new URL("https://api.opendatadsl.com/api/object");
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) u.openConnection();
con.setRequestMethod("GET");
con.setRequestProperty("Authorization", "Bearer " + token);
int status = con.getResponseCode();
if (status == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
content.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
System.out.println(content.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("FAILED: status is " + status);
}
Token expiry
The token has a lifetime of around an hour, which means if you are running an application and making service requests which go beyond the token expiry time, you will need to request a new token.