Data Monitoring 🆕
This guide gives detailed information about best-practices for utilising the data monitoring capabilities of the OpenDataDSL platform.
Monitoring Terminology
Monitoring of the loading of data is organised using the following entities:
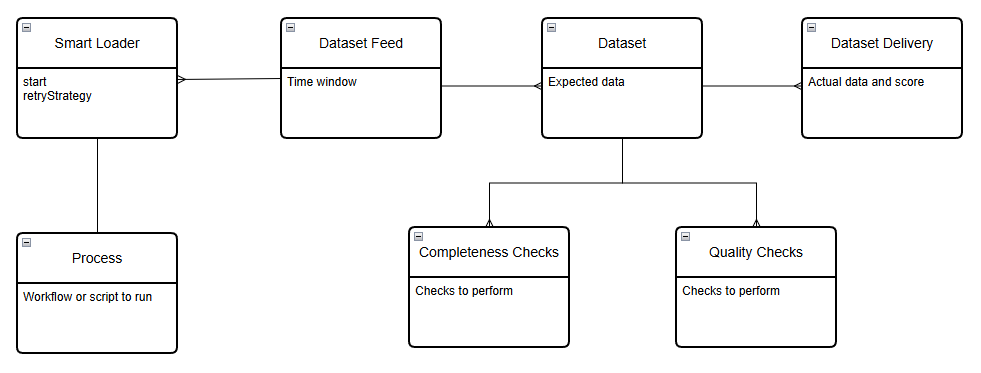
Smart Loader
A smart loader runs the defined process until all datasets are complete according to the completeness criteria. It uses a retryStrategy to determine how often to run the process.
Process
A process defines the workflow or script that is run to extract, transform and load data into the platform.
Dataset feed
A dataset feed is a configuration which defines the time window that you expect to receive all the data for a specific feed.
The identifier for a dataset feed is of the following format:
{provider id}.{feed id}
e.g. ICE.IFEU
Dataset
A dataset is an individual product within a dataset feed, this defines the quantity of data we expect to receive on a daily basis.
The identifier for a dataset feed is of the following format:
{provider id}.{feed id}.{product id}
e.g. ICE.IFEU.B
Dataset delivery
A dataset delivery is a record of all information regarding the process of getting the data for a dataset for a single day. It also calculates a score which identifies how well the process worked for each day.
The identifier for a dataset delivery is of the following format:
{provider id}.{feed id}.{product id}:{ondate}
e.g. ICE.IFEU.B:2024-06-12
Completeness Checks
These are advanced checks that are run on the raw data to make more targeted checks to ensure completeness.
Quality Checks
Quality checks are used to check the data to ensure it conforms to your expectations of values for this dataset.
A check consists of:
- name - The free-form name you want to give to this check, e.g.
Check for zero values - script - The name of the script to use for the expression - can be empty.
- expression - The expression to use to run the check. This is usually the function call, e.g.
zeroCheck(['SETTLEMENT_PRICE'])
You can also define a group of checks and add this onto the dataset.
Scoring
Every day that dataset loading occurs, a score is calculated which is a measurement used to indicate how well the process worked that day.
The scores are as follows:
- 4 - Data was loaded on time
- 3 - Data was maximum of 1 hour late
- 2 - Data was between 1 hour and 4 hours late
- 1 - Data was more than 4 hours late
- 0 - No data was expected, e.g. a holiday
Monitoring Lifecycle
The dataset delivery record represents the lifecycle for the dataset loading for a single day.
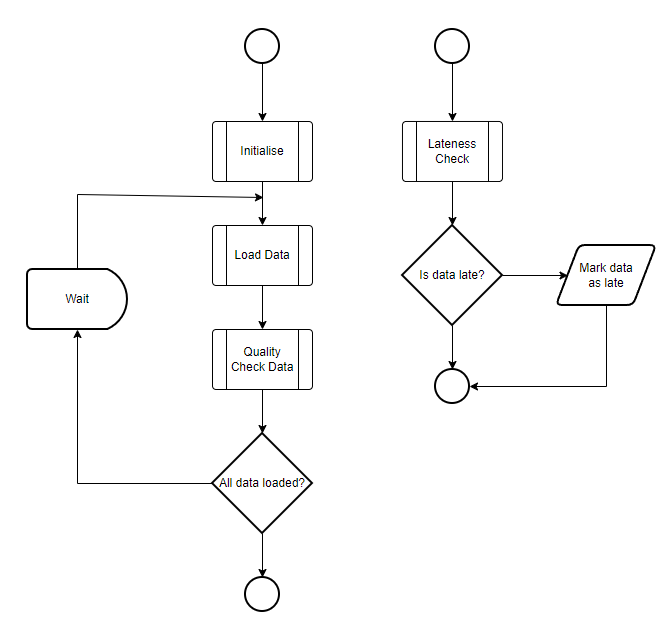
Initialisation
Each day begins with an initialisation of the dataset delivery record. This sets the following default values:
- status - waiting
- score - 4 (0 if it is a holiday) ( any lateness will start reducing that number)
- complete - false
- initialised - the timestamp of when the intialisation was run
Data loaded
When data is loaded that includes a _dsid property, the following occurs:
- Check for corrections - if the data for this data was previously loaded, it is checked to see if any of the values have changed.
- Calculate metrics
- Determine the quantity of tenors by tenor type loaded during this update
- Determine if all the expected tenors have been loaded - completeness
- Run any advanced completeness checks configured on the dataset to finalise completeness
- Update the timeline and delivery information in the dataset delivery
- Update the status to either partial (if not late) or loaded
Quality checks
Any quality checks that have been configured on the dataset are triggered after data has been loaded. The quality checks are always performed on the entire dataset, not just the most recently loaded.
Check for lateness
Periodically, a process runs that determines if any datasets are late according to the dataset feed time window.
If a dataset is determined to be late (or missing), the dataset delivery score is updated and an alert record is sent to subscriptions.
The lateness check also checks the missing time if it is configured, if the current time is beyond the missing time and it is a smart loader, the smart loader is halted and manual intervention is required.
Using the Dataset Monitoring API
This section guides you through using the dataset monitoring features.
Datasets and Dataset Feeds
Datasets and dataset feeds are 'managed' in 3 different locations:
- private - these are configured and managed by your company
- common - these are configured and managed by us, you will only see the common datasets you have access to
- public - these are configured and managed by us, you have access to all of these
Managing private datasets and dataset feeds
With private datasets, you can configure everything about the dataset and dataset feed, specifically:
- Dataset ID
As mentioned above, the dataset id comprises 3 sections: provider, feed and product. For private datasets, it is recommended to set the provider to a short-form version of your company name, e.g. for OpenDataDSL we use ODSL
- Expected tenors
You can either manually enter the list of expected tenors or if you have already loaded some data, you can get the system to calculate the minimum actual loaded tenors
- Expected checks
You can optionally add checks to determine if the dataset is complete as an addition to the simple minimum expected tenor check
- Calendar
This the the calendar that defines the days that you expect this data to be available, any non-calendar days are marked as holidays
- Timings
You can specify the time window when you expect the data to be ready to collect or be loaded into the system
- Checks
You can specify the quality checks you want to perform on the data loaded to this dataset
Examples
- OpenDataDSL
- REST API
An example of creating a private dataset feed
dsf = object as DatasetFeed
dsid = "ODSL.TRADER2"
name = "ODSL Trader2"
calendar = "BUSINESS"
timezone = "Europe/London"
time = "19:00 EU1"
late = "21:00 EU1"
end
save dsf
An example of creating a private dataset
ds = object as Dataset
dsid = "ODSL.TRADER2.NBP"
name = "Trader2 NBP Prices"
expected = SimpleObject()
end
ds.expected.set("*",12)
ds.expected.set("Month", 12)
save ds
An example of creating a private dataset with expected checks
ds = object as Dataset
dsid = "ODSL.DS.TEST"
source = "private"
name = "ODSL test dataset"
end
// Add simple expected checks
ds.expected = SimpleObject()
ds.expected.set("*", 2)
ds.expected.set("CalendarDay", 2)
ds.expected.set("Month", 2)
// Add advanced checks
cc1 = SimpleObject()
cc1.type = "function"
cc1.script = "#DatasetCompletenessChecks"
cc1.name = "Check for M01"
cc1.expression = "hasTenor('M01')"
ds.expectedChecks = [cc1]
// Add quality checks
check1 = SimpleObject()
check1.type = "function"
check1.script = "#QualityCheckDatasets"
check1.name = "Check for zero values"
check1.expression = "zeroCheck('SETTLEMENT_PRICE')"
// Add a quality check group
check2 = SimpleObject()
check2.type = "group"
check2.name = "My Dataset Quality Checks"
check2.group = "MY.QUALITY"
ds.checks = [check1, check2]
save ds
An example of creating a private dataset feed
POST {{url}}/dataset/v1/feed
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
{
"_id": "ODSL.TRADER1",
"calendar": "BUSINESS",
"time": "16:00 EU1",
"late": "19:00 EU1"
}
An example of creating a private dataset
POST {{url}}/dataset/v1/info
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
{
"_id": "ODSL.TRADER1.NBP",
"expected": {
"*": 12,
"Month": 12
}
}
An example of creating a private dataset with expected checks
POST {{url}}/dataset/v1/info
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
{
"_id": "ODSL.TRADER1.NBP",
"expected": {
"*": 12,
"Month": 12
},
"expectedChecks": [
{
"type": "function",
"script":"scripts-ds-quality",
"name":"has tenor M00",
"expression": "hasTenor('M00')"
}
],
"checks": [
{
"type":"function",
"script":"#QualityCheckDatasets",
"name":"Check for zero values",
"expression":"zeroCheck('SETTLEMENT_PRICE')"
},
{
"type":"group",
"name":"My Quality Group",
"group":"MY.GROUP"
}
]
}
Managing public and common datasets and dataset feeds
If you want to add public and common datasets into your monitoring, you can create references to them in your private database.
With public and common datasets, you can only configure the following:
- Checks
You can specify the quality checks you want to perform on the data loaded to this dataset
- Category
You can specify a category that you want to group datasets into
- Priority
You can specify a priority for this dataset from highest, high, medium, low, lowest to group and filter by
Examples
- OpenDataDSL
- REST API
Getting a list of all the available datasets
print ${dataset:"allds"}
Creating a reference to a common dataset
ds = object as Dataset
dsid = "ICE.NDEX.NLB"
source = "common"
end
save ds
Removing a reference to a common dataset
delete ${dataset:"info/ICE.NDEX.NLB"}
Getting a list of all the available datasets, projecting the id, name and source
GET {{url}}/dataset/v1/allds
?_project=name,source
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
Creating a reference to a common dataset with our own custom quality checks
POST {{url}}/dataset/v1/info
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
{
"_id": "ICE.NDEX.NLB",
"source":"common",
"checks": [
{
"type": "function",
"name": "Check for negative values",
"script": "#QualityCheckDatasets",
"expression": "negativeCheck('SETTLEMENT_PRICE')"
}
],
"category": "OIL",
"priority": "low"
}
}
}
Removing a reference to a common dataset
DELETE {{url}}/dataset/v1/info/ICE.NDEX.NLB
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
Dataset Deliveries
You can retrieve the delivery information for any datasets that you are monitoring. Any specific quality check results that you have added will also be shown in the dataset delivery information.
Examples
- OpenDataDSL
- REST API
// Get all dataset deliveries for the current ondate
find ${dataset:"delivery"}
// Get all dataset deliveries for a specific ondate
find ${dataset:"delivery/2024-06-25"}
Get all dataset deliveries for the current ondate
GET {{url}}/dataset/v1/delivery
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
Get all dataset deliveries for a specific ondate
GET {{url}}/dataset/v1/delivery/2024-06-25
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
Dataset Quality Check Groups
You can create quality check groups containing an array of checks, this group can then be added onto a dataset. Any specific quality check results that you have added will also be shown in the dataset delivery information.
Examples
- OpenDataDSL
- REST API
// Create a quality group
g = QualityGroup()
g.type = "quality"
g.category = "dataset"
g.name = "ICE.NDEX.QUALITY"
g.description = "ICE Endex Dataset Quality Checks"
g.script = "#QualityCheckDatasets"
g.addCheck("Check for zero values", "zeroCheck(['SETTLEMENT_PRICE'])")
save g
Create a quality group
POST {{url}}/group/v1
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
{
"type": "quality",
"category": "dataset",
"name": "ICE.NDEX.QUALITY",
"description": "ICE Endex Dataset Quality Checks",
"script": "#QualityCheckDatasets",
"checks": [
{
"name": "Check for zero values",
"expression": "zeroCheck(['SETTLEMENT_PRICE'])"
}
]
}
Get a group
GET {{url}}/group/v1/quality/ICE.NDEX.QUALITY
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
Rollback changes to a quality group
DELETE {{url}}/group/v1/quality/ICE.NDEX.QUALITY
Authorization: Bearer {{token}}
Dataset Quality Scripts
The ODSL scripts you create contain functions to perform quality checks on datasets.
The functions have access to the following variables:
- #DSID - The string dataset id
- #ONDATE - The date for the dataset update
- #LOG - A log object to place all the failure information
- #EVENTS - A list of all the events for this dataset update
All scripts to be used for dataset quality checks need to have a category dataset-quality, you can do this by adding the following to the top of your script:
/**
* @category dataset-quality
*/
Example Functions
Check to see if any specific properties are zero
Example expression: zeroCheck(['value'])
function zeroCheck(properties)
zeroCheck = "valid"
#LOG.failures = []
print "Checking " + #EVENTS.size() + " events for dataset: " + #DSID + " for " + #ONDATE
for pc in #EVENTS
for p in properties
// Test for zero value
v = variable(pc, p)
tenor = variable(pc, "absolute")
if v.isZero()
zeroCheck = "failed"
#LOG.failures.add("Zero value for " + tenor)
end
next
next
end
Dataset Completeness Check Scripts
The ODSL scripts you create contain functions to perform expected checks on datasets.
The functions have access to the following variables:
- #DSID - The string dataset id
- #ONDATE - The date for the dataset update
- #LOG - A log object to place all the failure information
- #EVENTS - A list of all the events for this dataset update
All scripts to be used for dataset completeness checks need to have a category dataset-completeness, you can do this by adding the following to the top of your script:
/**
* @category dataset-completeness
*/
Example Functions
Check to ensure a specific named tenor is present
Example expression: hasTenor('M00')
function hasTenor(tenor)
hasTenor = "failed"
#LOG.failures = ["Missing " + tenor + " tenor"]
for ev in #EVENTS
if ev.relative == tenor
hasTenor = "valid"
#LOG.failures = []
log info tenor + " found"
end
next
end
Check for number of daily tenors dependent on the day of the week
This check determines the number of expected tenors based on the day of the week. If the day matches the startday, the max tenors are expected, and it decreases as the week progresses, e.g.
Using the expression: rollingOffDayTenors('MONDAY', 14, 'BUSINESS')
| Day of week | Expected Tenors |
|---|---|
| Monday | 14 |
| Tuesday | 13 |
| Wednesday | 12 |
| Thursday | 11 |
| Friday | 10 |
function rollingOffDayTenors(startday, max, calendar)
rollingOffDayTenors = "valid"
test = Date(#ONDATE)
dow = test.dow
log info "Day of week = " + dow
cal = Calendar(calendar)
expected = max
while dow != startday
test = cal.previous(test)
dow = test.dow
expected = expected - 1
end
log info "Expected number of daily tenors = " + expected
actual = 0
for ev in #EVENTS
if startsWith(ev.relative,"D")
actual = actual + 1
end
next
if actual < expected
log fatal "Actual number of daily tenors = " + actual
#LOG.failures = ["Expecting " + expected + " daily tenors, got " + actual]
rollingOffDayTenors = "failed"
end
end